
Section 15 The Bootstrap
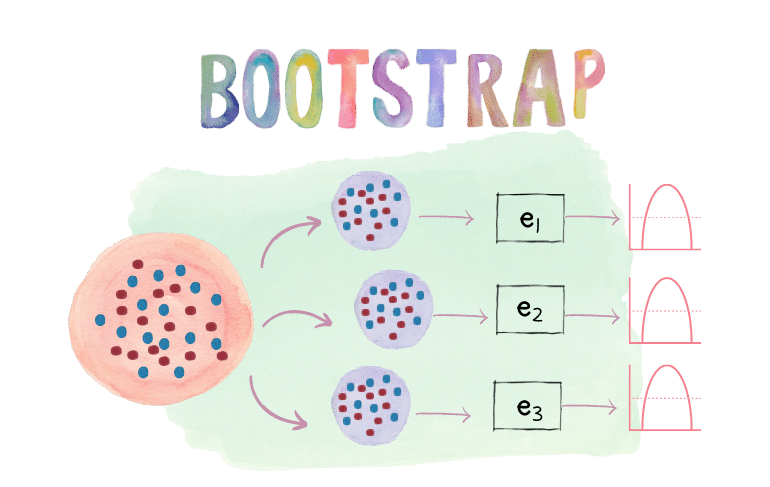
The bootstrap is a widely applicable and extremely powerful statistical tool that can be used to quantify the uncertainty associated with a given estimator or statistical learning method.
The bootstrap method is a statistical technique for estimating quantities about a population by averaging estimates from multiple small data samples.
Importantly, samples are constructed by drawing observations from a large data sample one at a time and returning them to the data sample after they have been chosen. This allows a given observation to be included in a given small sample more than once. This approach to sampling is called sampling with replacement.
The process for building one sample can be summarized as follows:
Choose the size of the sample.
While the size of the sample is less than the chosen size:
Randomly select an observation from the dataset
Add it to the sample
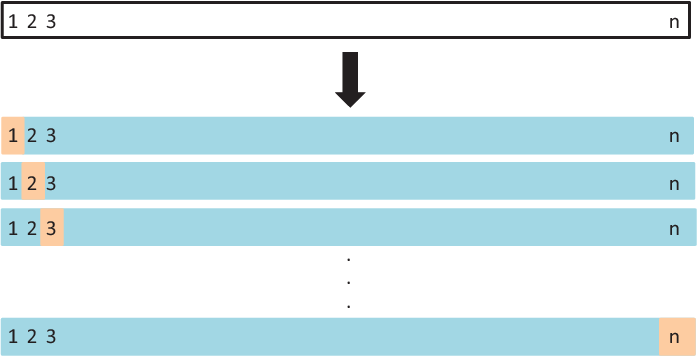
Figure 15.1: A graphical illustration of the bootstrap approach on a small sample containing n=3 observation
A graphical illustration of the bootstrap approach is illustrated in Figure 15.1. Each bootstrap data set contains \(n\) observations, sampled with replacement from the original data set. Each bootstrap data set is used to obtain an estimate of \(\alpha\).